Garlic has been recognized for centuries as a powerful natural remedy with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that may support ear health. This exploration examines the biochemical mechanisms underlying garlic’s therapeutic potential and its applications in addressing common auditory concerns.
Bioactive Compounds in Garlic: Molecular Foundation
Garlic (Allium sativum) contains a complex array of organosulfur compounds that confer its medicinal properties. The primary bioactive constituent, allicin, forms through enzymatic conversion when garlic cells are crushed or damaged. This volatile compound, along with ajoene, diallyl disulfide, and S-allylcysteine, demonstrates significant antimicrobial activity against various bacterial and fungal pathogens commonly implicated in ear infections.
The antimicrobial efficacy of garlic derives from allicin’s ability to interact with thiol groups in bacterial enzymes, disrupting essential metabolic processes. Studies have documented garlic’s effectiveness against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa—organisms frequently associated with otitis externa and otitis media. Additionally, garlic exhibits antifungal properties against Candida species and Aspergillus, which can colonize the ear canal under certain conditions.
Beyond antimicrobial effects, garlic contains flavonoids and selenium compounds that contribute to its anti-inflammatory profile. These constituents modulate inflammatory pathways by inhibiting cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase enzymes, potentially reducing pain and swelling associated with ear discomfort.
Mechanisms of Action in Auditory Tissues
The therapeutic application of garlic for ear health operates through multiple physiological mechanisms. When applied topically as an infused oil preparation, garlic’s volatile compounds penetrate the external auditory canal, creating an environment hostile to pathogenic microorganisms while maintaining compatibility with the delicate epithelial lining.
The anti-inflammatory compounds in garlic may help reduce edema in the ear canal and tympanic membrane, facilitating drainage of accumulated fluids and improving ventilation of the middle ear space. This effect proves particularly relevant in cases of mild inflammation or congestion where fluid accumulation creates discomfort without acute infection.
Garlic also demonstrates analgesic properties through mechanisms that remain partially elucidated. Current evidence suggests that certain organosulfur compounds may interact with pain receptors and modulate neurotransmitter release, providing symptomatic relief from ear discomfort. However, these effects appear modest compared to pharmaceutical analgesics and should be considered complementary rather than substitutive.
Traditional Applications and Modern Adaptations
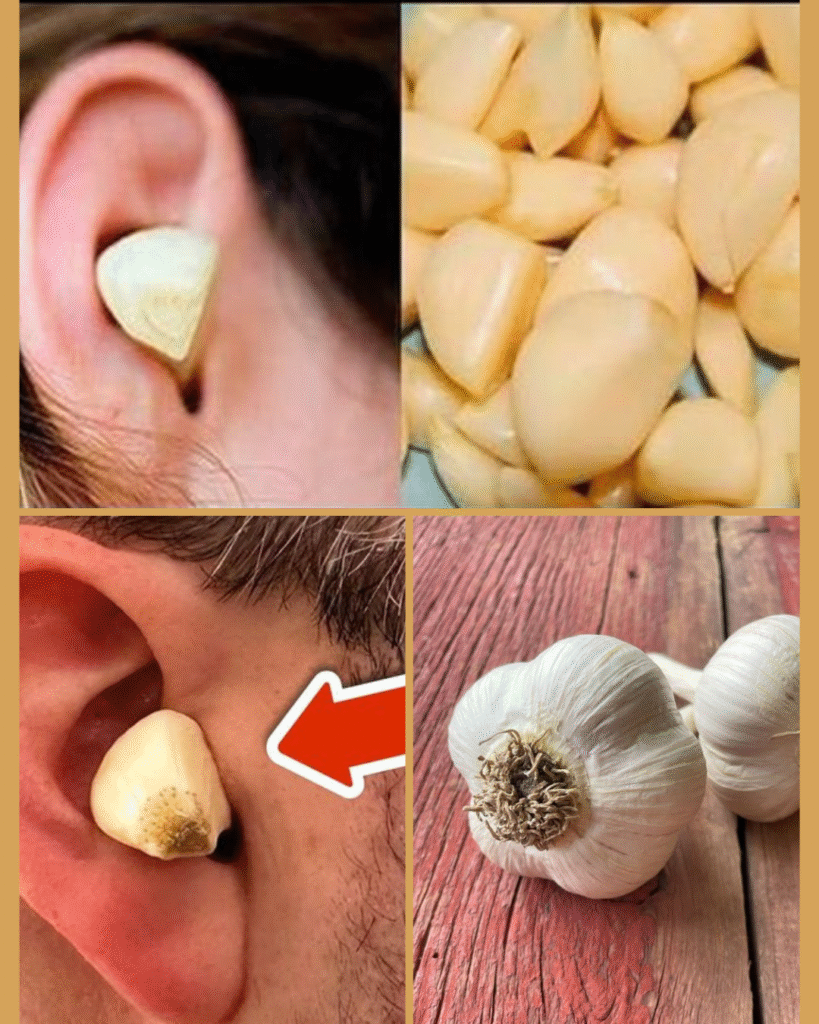
Historical medical traditions across Mediterranean, Asian, and Middle Eastern cultures have employed garlic preparations for ear ailments. Traditional methods typically involved crushing fresh garlic cloves and mixing the expressed juice with carrier oils such as olive oil or sesame oil. The mixture would be gently warmed and applied dropwise into the affected ear canal.
Modern adaptations of these traditional practices maintain the fundamental principles while incorporating considerations for safety and standardization. Contemporary garlic ear oil preparations often involve a longer infusion process where crushed garlic is steeped in warm carrier oil for several hours, allowing extraction of therapeutic compounds while minimizing tissue irritation from excessively concentrated fresh garlic juice.
The preparation method significantly influences the final product’s composition and therapeutic profile. Cold infusion preserves heat-sensitive compounds but requires extended steeping times, while gentle warming accelerates extraction but may degrade certain volatile constituents. Optimal preparation balances extraction efficiency with compound stability, typically achieving this through brief warming to approximately 40-50 degrees Celsius followed by prolonged room-temperature infusion.
Clinical Considerations and Application Parameters
When considering garlic preparations for ear health support, several clinical parameters warrant attention. The integrity of the tympanic membrane represents a critical consideration—application of any substance into the ear canal when membrane perforation is suspected or confirmed poses risks of middle ear irritation and potential hearing complications. Direct visualization by a healthcare professional should precede any topical ear treatment when infection or injury is suspected.
For external ear conditions without membrane involvement, garlic-infused oil may be applied using careful technique. The preparation should be warmed to approximately body temperature to avoid thermal shock to the ear canal. Application involves tilting the head to position the affected ear upward, instilling 2-3 drops of the preparation, and maintaining the position for several minutes to allow penetration along the canal walls.
The concentration of garlic in carrier oil preparations requires calibration to balance efficacy with tolerability. Excessive concentration may irritate the sensitive epithelium of the ear canal, particularly in individuals with compromised skin integrity or heightened sensitivity. A general guideline suggests using 1-2 crushed garlic cloves per 30 milliliters of carrier oil, though individual tolerance varies considerably.
Comparative Analysis: Garlic Versus Conventional Interventions
The therapeutic positioning of garlic preparations in the management of ear conditions requires contextual understanding of their capabilities and limitations relative to conventional medical interventions. For mild external ear discomfort without signs of acute bacterial infection, garlic oil may provide supportive care through its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. However, its efficacy remains substantially lower than topical antibiotic preparations for established bacterial infections.
Research comparing garlic extracts to pharmaceutical antibiotics demonstrates that while garlic exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity in vitro, its potency against specific pathogens typically measures several orders of magnitude lower than targeted antibiotics. This differential becomes clinically significant when treating acute otitis media or severe otitis externa, conditions requiring reliable pathogen eradication to prevent complications.
The anti-inflammatory effects of garlic, while measurable, do not approach the potency of corticosteroid preparations commonly used for inflammatory ear conditions. For significant inflammation or allergic responses affecting the ear, pharmaceutical interventions remain the evidence-based standard. Garlic preparations may offer modest symptomatic support but should not delay appropriate medical evaluation when symptoms persist or worsen.
Safety Profile and Contraindications
The safety profile of topical garlic preparations for ear application demonstrates generally favorable characteristics when used appropriately, though certain considerations and contraindications merit attention. Contact dermatitis represents the most commonly reported adverse effect, manifesting as redness, itching, and burning sensations in the ear canal. This reaction typically results from individual sensitivity to organosulfur compounds or excessive concentration in the preparation.
Fresh garlic juice, particularly in undiluted or minimally diluted form, demonstrates significant potential for chemical irritation due to its high allicin content. The concentration of bioactive compounds in fresh preparations substantially exceeds that of properly infused oils, increasing the risk of epithelial damage. Cases of chemical burns from inappropriate application of concentrated garlic preparations to the ear canal have been documented in medical literature, underscoring the importance of proper dilution and preparation methods.
Absolute contraindications for topical garlic ear preparations include suspected or confirmed tympanic membrane perforation, presence of tympanostomy tubes, active drainage from the ear, severe pain suggesting acute infection, and known allergy to Allium species. Relative contraindications encompass conditions where the risk-benefit profile becomes less favorable, including diabetes mellitus with peripheral sensory neuropathy, immunocompromised states, and age extremes where clinical assessment proves more challenging.
Integration Within Comprehensive Ear Health Strategies
The appropriate integration of garlic preparations within a comprehensive approach to ear health requires understanding their role as complementary rather than primary interventions. For prevention-oriented strategies, maintaining optimal ear hygiene, avoiding insertion of objects into the ear canal, and managing underlying conditions that predispose to ear problems form the foundation of sustainable ear health.
Garlic preparations may serve supportively in situations involving minor ear discomfort without signs of infection, post-swim sensation of water retention with mild irritation, or as part of a broader anti-inflammatory dietary approach for individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions. The systemic consumption of garlic as part of a balanced diet may contribute to overall immune function and inflammatory modulation, though direct topical application targets local ear tissues more specifically.
Environmental factors significantly influence ear health outcomes. Excessive moisture exposure, particularly in swimmers or individuals in humid climates, creates conditions favorable for microbial proliferation. Gentle drying of the external ear canal after water exposure, use of properly fitted ear protection during water activities, and avoidance of aggressive cleaning practices that damage the protective cerumen layer all contribute to maintaining optimal ear health.
Biochemical Stability and Storage Considerations
The stability of garlic-infused oil preparations depends on multiple factors including the initial garlic concentration, carrier oil selection, storage conditions, and time since preparation. Allicin and related organosulfur compounds demonstrate inherent instability, particularly in the presence of heat, light, and oxygen. This instability necessitates careful attention to preparation and storage protocols to maintain therapeutic activity.
Carrier oil selection influences both the extraction efficiency of garlic compounds and the preparation’s shelf stability. Oils with higher antioxidant content, such as olive oil rich in vitamin E and polyphenols, demonstrate enhanced stability compared to more readily oxidizable oils. Dark glass containers stored in cool conditions away from direct light substantially extend the usable lifespan of garlic oil preparations, typically maintaining reasonable potency for 1-2 weeks when properly stored.
Refrigeration presents trade-offs in storage strategy. While cold temperatures slow oxidative degradation and microbial growth, refrigerated preparations require warming to body temperature before application to avoid discomfort. Additionally, condensation issues may arise when transitioning cold preparations to ambient temperature environments. Room temperature storage in dark, cool locations often provides an acceptable compromise for preparations intended for use within a week of formulation.
Emerging Research Directions and Mechanistic Investigations
Current research into garlic’s therapeutic applications continues to elucidate novel mechanisms and potential clinical applications. Recent investigations have identified specific organosulfur compounds that demonstrate selective activity against biofilm-forming bacteria, a characteristic particularly relevant to chronic ear infections where biofilms contribute to treatment resistance and infection persistence.
Advanced analytical techniques including gas chromatography-mass spectrometry have enabled detailed characterization of garlic preparation compositions, revealing that processing methods significantly alter the profile of bioactive compounds. This research suggests that optimization of preparation techniques could enhance therapeutic efficacy while minimizing irritation potential, though clinical validation of these hypotheses remains limited.
The interaction between garlic compounds and the ear’s indigenous microbiota represents another emerging research area. The external ear canal hosts a diverse microbial community that generally contributes to ear health through competitive exclusion of pathogens and production of antimicrobial substances. Understanding how garlic preparations influence this microbiome balance could inform more nuanced application strategies that support beneficial commensals while suppressing pathogenic organisms.
Pediatric Considerations and Developmental Factors
The application of garlic preparations for ear conditions in pediatric populations requires additional considerations reflecting anatomical and physiological differences. Children’s ear canals demonstrate smaller dimensions, different angulation relative to adults, and epithelium that may exhibit heightened sensitivity to topical preparations. These factors collectively increase both the challenge of appropriate application and the potential for adverse effects from improper use.
Acute otitis media occurs with substantially higher frequency in children compared to adults, reflecting anatomical features of the pediatric Eustachian tube that compromise drainage and ventilation. While parents may seek natural alternatives to conventional treatments, the risk of complications from inadequately treated bacterial ear infections in children—including hearing impairment, mastoiditis, and rare but serious intracranial complications—necessitates prioritization of evidence-based medical evaluation and treatment.
For minor external ear discomfort in children without signs of infection, appropriately diluted garlic oil preparations may offer supportive care under parental supervision. However, the challenge of assessing symptom severity in young children who cannot articulate their discomfort precisely argues for a conservative approach with lower thresholds for professional evaluation. Any persistent symptoms, fever, significant pain, or behavioral changes suggesting serious discomfort warrant prompt medical assessment rather than continued home management.
Holistic Framework: Nutrition, Immunity, and Ear Health
The relationship between garlic consumption, immune function, and ear health extends beyond topical applications to encompass broader nutritional and immunological considerations. Regular dietary inclusion of garlic and related Allium vegetables contributes to overall immune competence through multiple pathways, including enhanced natural killer cell activity, modulation of cytokine production, and support for gut microbiome diversity.
The gut-immune axis plays an underappreciated role in susceptibility to respiratory and ear infections. A robust and diverse intestinal microbiome contributes to systemic immune regulation and may influence the frequency and severity of upper respiratory infections that commonly precipitate secondary ear involvement. Garlic’s prebiotic properties—derived from inulin and fructooligosaccharides content—support beneficial intestinal bacterial populations, potentially contributing to reduced infection susceptibility through this indirect mechanism.
Nutritional status more broadly influences ear health outcomes, with deficiencies in zinc, vitamin A, and vitamin D associated with increased infection susceptibility and compromised mucosal immunity. A dietary pattern emphasizing diverse plant foods including garlic, adequate protein for immune cell production, and attention to micronutrient adequacy provides a foundation for optimal immune function that extends to ear health resilience.
This comprehensive exploration demonstrates that garlic preparations offer potential supportive benefits for ear health through documented antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, while recognizing important limitations and safety considerations. Their optimal use occurs within an integrative framework that prioritizes appropriate medical evaluation when indicated, employs proper preparation and application techniques, and situates topical interventions within broader strategies for immune support and ear health maintenance.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Source: National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), National Institutes of Health – Research on garlic’s antimicrobial and therapeutic properties in complementary medicine approaches.